Accounts payable is any sum of money owed by a business to its suppliers shown as a liability on a company's balance sheet. In simple words, when you buy goods or services with an arrangement to pay at a later date, such amount till it is paid is referred to as accounts payable.
Accounts payable is also called as bills payable and the total amount that a company is liable to pay is shown as liability under the head ‘sundry creditor’ in the balance sheet.
Example of accounts payable
Max Enterprises purchased goods worth 1,00,000 from Ace Traders. Ace Traders offered a credit period of 30 days within which the bill should be paid by Max Enterprises.
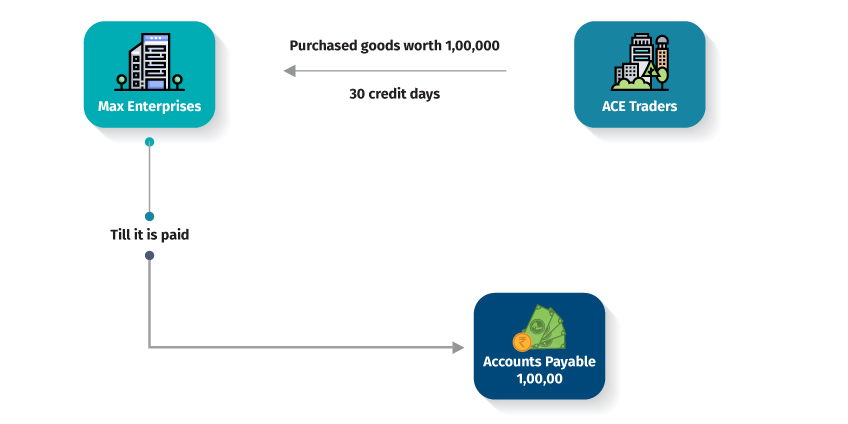
Here, till the date Max Enterprises pays Ace Traders, the amount of 1,00,000 will be called as accounts payables and shown as liability towards creditors in the balance sheet.
Importance of accounts payable
Any business, whether manufacturing or trading, need to procure the goods or services from their suppliers and most times, you will be offered to pay on a later date. This results in a major source of cash outflows towards the trade payable and therefore businesses must manage it efficiently.
While accounts payable are short-term liabilities that need to be honoured within a specific date, any delayed payment will attract additional charges in the form of interest and later payment charges. Also, delayed payment may create ill-feeling and impacts the credibility of the business which in turn leads to disruption of the supplies.
Accounts payables involve a carrying cost, not just the additional charges for delayed payments but also the other form of cost. Find out by reading ‘Cost of Accounts Payables’
Accounts payable process
An accounts payable process has many moving parts, potentially manual process steps, and multiple people across the organization involved.
The accounts payable process starts right after you have decided to procure the goods or services on a credit basis. The following is the accounts payable process that you get to see in most of the business
- Evaluating the credit policy of the supplier in terms of credit days allowed, delayed payment charges, cash discount on early payment etc.
- Finalize the supplier and procure the goods in accordance with the procurement process followed by your business
- Once the goods are received, account the invoice in the books
- Need to pay special attention to record the due date within which the bills need to be paid
- Track the bills that are nearing the due date and plan to clear. Accounts payables and the ageing report will be of great help here.
- Account the payments made in the books and it will good practice to keep a track the invoices against which the payments are honoured
- Send the acknowledgements such as payment advice or any other statement to inform the supplier about the payment that is made.
Taking full advantage of the credit days will help you to manage the cash flow efficiently. While it is easy but not tracking and knowing when to honour bills will prove to be a disadvantage to the business.



Comments
Post a Comment