It would not be that easy to be on top of the balance sheet if you are not familiar with certain fundamentals of balance sheet. In this article, we will explore the balance sheet right from basics to analyzing it. It’s not too difficult to understand if are willing to spend a few minutes in learning the concepts of balance sheet.
What is Balance Sheet?
A balance sheet, also known as a "statement of financial position," reveals the details of the company's assets, liabilities and the amount owned by shareholders. Balance Sheet tells you the assets you own, the amount of money you owe to others and the owner’s equity. This broadly consists of liabilities and assets. This financial statement helps you to analyze how companies are funding capital assets and operations as well as current investor information.
Balance Sheet Equations
As the name suggests, the balances of total liabilities and assets owned by the business always match. Meaning, the total value of assets always adds up to the total liabilities of the business. Basis this, the balance sheet equation or formula can be drawn as below:
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity
The above balance sheet equation simply tells you that all the assets owned by the business are either sponsored using the owners’ equity or the amount which company should owe others like suppliers or borrowings like Loans. Thus, when you add-up, assets will be always equal to total liabilities which includes owners’ equity.
Similarly, you can draw a balance sheet equation for liabilities
Liabilities = Assets – Owner’s Equity
This is no brainer. The difference of assets and owner’s investment into business is your liabilities which you owe others in the form of payables to suppliers, banks etc.
Just like above, you can formulate the balance sheet equation for owner’s Equity.
Owners’ Equity = Assets – Liabilities
The above equation states the value of assets owned purely by owner equity. In another way, if you sell all your assets and after paying back the debts, the left-over portion would be the owner’s equity. That’s the money you put into your business including the accumulated profits added to equity.
Format of Balance Sheet
The format of the balance sheet consists of liabilities on one side and assets on the other sides. In some cases, the balance sheet is prepared in vertical format representing liabilities on top followed with assets. The visuals of balance sheet formats are given below for better understanding.
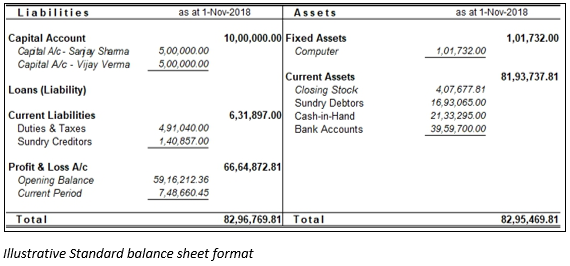

Components of Balance Sheet
As you can see in the balance sheet format, it consists of 2 broad components: Assets and Liabilities as discussed below:
Assets
Something that an entity has acquired or purchased and owned, regarded as having value and available to meet debts, commitments or legacies. Assets are further broadly classified as:
- Fixed Assets:Assets which are purchased for long-term use and are not likely to be converted quickly into cash, such as land, buildings, and equipment.
- Current Assets:A current asset is an item on an entity's balance sheet that is either cash, a cash equivalent, or which can be converted into cash within one year. Examples of current assets are, Cash, Bank balances, Investments, Deposits, Accounts receivables and Inventory
Liabilities
Liabilities are the obligations or Debts payable by the enterprises in future in the form of money or goods. Liabilities are the outsider’s equity. Liabilities are further broadly classified as:
- Equity or Capital:Money invested in the business to generate income.
- Loans & Borrowings:Money borrowed from a financial institution or from others to be utilized in business for generating income and managing the day to day affairs of the business. Loans are regarded as credit granted by the lender where the money is disbursed, and its recovery is made on a later date in a lump sum or in instalment. Ex: Bank Overdraft, Term Loan.
- Current Liabilities:Current liabilities are debts or obligations payable within a short period of time or one year. Ex: short term debt, trade payables, taxes due, accrued expenses.
Now that you have understood the basics of the balance sheet, it becomes easier for you to prepare a balance sheet and then reading through it. Preparation of balance sheet is not that difficult; it just requires you to report the closing balance of affected accounts. But gathering all the balances into a balance sheet is not that simple. Read our article ‘How to Prepare Balance Sheet and Read it?’ to know the complete process of preparing and analysing it.



Comments
Post a Comment